| RIP v 2 224.0.09 | EIGRP 224.0.0.10 | OSPF 224.0.0.5 224.0.06 |
| Базовые настройки router(conf)# router rip router(conf-router)# version 2 router(conf-router)# network <классовая сеть> Команда network указывает только на каких интерфейсах включить RIP, а фактическая сеть и маска будет взята из настроек интерфейса. Маршрут по умолчанию R1(config-router)# default-information originate [route-map <map-name>] Если в route table есть default static route, то можно его распространить : R1(config-router)# redistribute static [metric <metric>] [route-map <map-name>] Настройка суммарного маршрута: R1(config-if)# ip summary-address rip n.add SM Удалить можно все маршруты: router# clear ip route * Triggered extension to RIP — дополнительный функционал, который позволяет R IP отправлять полную информацию о всех маршрутах только один раз и после этого не отправлять её. Функция разработана для demand circuit и описана в RFC 2091. Включается на интерфейсе командой ip rip triggered. TROUBLESHOOTING R1# show ip rip database R1# show ip route R1# show ip protocols | Задаем № Autonomous System.На всех Rx AuSys он должен быть одинаковый. теперь необходимо объявить непосредственно подключенные сети. R1(config)# router eigrp 1 Включение EIGRP на интерфейсах: R1(config-router)# network <network> [wildcard mask] <network> — непосредственно присоединенная сеть к маршрутизатору. Если в route table есть default static route, то можно его распространить : R1(config-router)# redistribute static [metric Маршрут по умолчанию EIGRP: R1(config)# ip default-network <network-number> Отключить автосуммирование: R1(config-router)#no auto-summary Суммарный маршрут настраивается на интерфейсе: R1(config-if)#ip summary-address eigrp <AS-number> <address> <mask> [admin-distance] Изменения интервала hello-пакетов: router(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp <asn> <seconds> Изменения hold-интервала: router(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp <asn> <seconds> R1(config-if)# bandwith (Kbps) TROUBLESHOOTING R1#sh ip eigrp neighbors: R1#sh ip eigrp neighbors detail R1# sh ip route eigrp R1#sh ip protocols R1#sh ip eigrp interfaces R1#sh ip eigrp topology R1# debug ip eigrp Настройка % bandwidth, к-й будет исп-вать EIGRP: R1(config-if)#ip bandwidth-percent eigrp <AS-number> <percent> | Сами прописываем cost на интерфейсе: R1(config-if)#ip ospf cost < > Назначаем приоритет на интерфейсе: R1(config-if)#ip ospf priority <0-255 > Router ID назначаем сами: R1(config-router)#router-id <ip-address> Если RID не был назначен нами, то он выбирается авт-ки, в зависимости от настроек роутера, по таким правилам: 1. Настроен один loopback-интерфейс и несколько интерфейсов с различными адресами: IP address loopback 0=Router ID. 2. Настроены Lo1, Lo2…Lo9 с IpAdd1, ApAdd2… ^ Наибольший IpAdd Lo = Router ID. 3. Настроены неск-ко интерфейсов с Ip Add: Наибольший Ip Add из всех акт.интерфейсов= RID. Включить OSPF на интерфейсах в соответствующих сетях: R1(config)# router ospf <process-id> R1(config-router)# network <network> <wildcard mask> area <area-id> Команда network 1)включает OSPF на интерфейсе, IP-адрес которого совпадает с указанной сетью и маской, 2) анонсирует сеть этого интерфейса через другие интерфейсы, на которых включен OSPF. Если в route table есть default static route, то можно его распространить : R1(config-router)# default-information originate Включение OSPF на интерфейсах: R1(config-if)# ip ospf <process-id> area <area-id> Изменение hello-интервала: R1(config-if)# ip ospf hello-interval <sec> Изменение dead-интервала: R1(config-if)# ip ospf dead-interval <sec> TROUBLESHOOTING R1# show ip route ospf R1# show ip ospf interface R1# show ip ospf interface brief R1# show ip ospf database Настройка аутентификации type 1 для зоны 1 (пароль надо задавать на интерфейсах): R1(config-router)# area 1 authentication |
вторник, 28 февраля 2012 г.
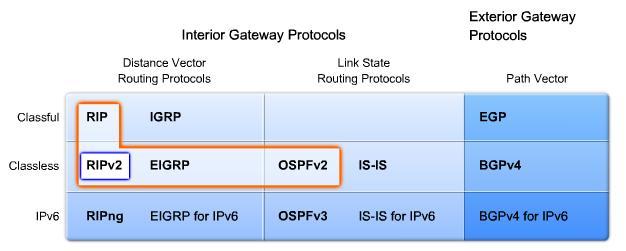
RIPv2. EIGRP. OSPF
География. Португалия.
Мне снится сон. Давно. Два-три раза в год. Это началось в средней школе. Не знаю причины или повода почему мне снится этот сон, но на утро моя душа поет.

... Солнце. Приморский город. спускаюсь с горы. Справа и слева от меня выбеленные двух-трех этажные дома с черепичной крышей. На окнах ставни. Запахи рынка. Специи. Я выхожу на смотровую площадку. Предо мной - океан. Я точно знаю, что это не море. Знаю. Атлантический Океан. Великий и безбрежный. мраморные ступени ведут меня прямо к воде. Синяя. Прозрачно синяя. В жизни, я никогда не видела такой воды. Она как сапфир. Манит своим цветом и спокойствием. Я знаю. Это - Португалия. Не понимаю откуда и с чего вдруг взялась эта уверенность, что я в Португалии. Я никогда там не была. Но я чувствую, что когда -нибудь я увижу это место не во сне, а на яву.
Португалия расположена в западной части Европейского континента. С юга ее омывает Гибралтарский пролив, на западе находится Атлантический океан, а с севера и востока граничит с Испанией. Климат диктуется Гольфстримом – субтропический, мягкий с температурой зимой не ниже +5, а летом достигает +30
Португалия в прошлом была великим королевством, во владения которой входили многие колонии.
Достопримечательности
Природные – Пляжи Агарви (юж. Провинция страны) и осторова Мадейра . Горячие источники.
коллекция скульптур XVI в.;
римский акведук; собор XII в. в романском стиле;
церковь Санта-Круз XVI в. Авейру;
музей римский скульптур и живописи XVI в. Лиссабон: национальный музей древнего искусства (живопись с XII по XIX в.);
музей современного искусства;
национальный музей естественной истории;
этнографический музей;
археологический музей;
морской музей;
музей Калоста Гульбенкиана с коллекцией предметов искусства с 2800 до н.э. до XX в.;
Се. готический собор XII в.;
монастырь иеронимитов (XVI в.), построенный в честь плавания в Индию Васко да Гама.
Брага: развалины римских храмов; амфитеатра и акведука; собор XII в., в котором похоронен Генрих Бургундский, отец первого португальского короля Альфонсо I; святыня Португалии церковь Дом-Хесус.
Порто: собор XII-XVIII вв.; гранитная башня Клериков XVIII в. высотой 75 м.
Сетубал: Церковь Санта-Мария XVI в. в готическом стиле. Римская архитектура: храм Дианы на Ю-В страны; развалины города Конимбрига на западном берегу.
Фуншал (о-в Мадейра): изобилие религиозной
архитектуры.
понедельник, 27 февраля 2012 г.
воскресенье, 26 февраля 2012 г.
CCNA Expl 2.Chapter 7. RIP v. 2
CCNA Exploration 2.Routing protocols and Consepts.
A loopback interface is a software-only interface that is used to emulate a physical interface.
- ideal for simulating multiple networks attached to the same router.

Null Interface -
R2(config)#ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
R2(config-router)#redistribute static
- Redistribution involves taking the routes from one routing source
and sending those routes to another routing source.
R2# debug ip rip
The show ip protocols command verifies that R2 is configured for RIPv1 but receives RIP messages for both versions.
R# show ip interface brief
R# show ip protocols
R# debug ip rip
R# ping
R# show running-config
The network statement does two things:
1. It enables the routing protocol to send and receive updates on any local interfaces that belong to that network.
2. It includes that network in its routing updates to its neighboring routers.
If there is a need or expectation for sending specific subnets and not just summarized routes, make sure that automatic summarization has been disabled.
A security concern of any routing protocol is the possibility of accepting invalid routing updates.
RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPF, IS-IS, and BGP can be configured to authenticate routing information.
=> Routers will only accept routing information from other routers that have been configured with the same password or authentication information.
RESUME.
RIP v.1 | RIP v.2 |
Distance vector routing protocol | |
classful routing protocol | classless routing protocol |
do not include the subnet mask with the network address in routing updates, which can cause problems with discontiguous subnets or networks that use Variable-Length Subnet Masking (VLSM). | subnet masks are included in the routing updates |
following features and limitations: | |
~ Use of holddown and other timers to help prevent routing loops. ~ Use of split horizon or split horizon with poison reverse to also help prevent routing loops. ~ Use of triggered updates when there is a change in the topology for faster convergence. ~ Max. hop count limit of 15 hops, with the hop count of 16 signifying an unreachable network. | |
A loopback interface is a software-only interface that is used to emulate a physical interface.
- ideal for simulating multiple networks attached to the same router.

Null Interface -
R2(config)#ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
R2(config-router)#redistribute static
- Redistribution involves taking the routes from one routing source
and sending those routes to another routing source.
R2# debug ip rip
The show ip protocols command verifies that R2 is configured for RIPv1 but receives RIP messages for both versions.
By default, RIPv2 automatically summarizes networks at major network boundaries, just like RIPv1.
R3(config-router)#no auto-summary - To modify the default RIPv2 behavior of automatic summarization (RIPv2).
Because classless routing protocols like RIPv2 can carry both the network address and the subnet mask, they do not need to summarize these networks to their classful addresses at major network boundaries. Therefore, classless routing protocols support VLSM.
There are several ways to verify and troubleshoot RIPv2. Many of the same commands used for RIPv2 can be used to verify and troubleshoot other routing protocols.
1. Make sure all of the links (interfaces) are up and operational.
2. Check the cabling.
3. Check to make sure you have the correct IP address and subnet mask on each interface.
4. Remove any unnecessary configuration commands that are no longer necessary or have been replaced by other commands.
R# show ip route
R# show ip interface brief
R# show ip protocols
R# debug ip rip
R# ping
R# show running-config
The network statement does two things:
1. It enables the routing protocol to send and receive updates on any local interfaces that belong to that network.
2. It includes that network in its routing updates to its neighboring routers.
If there is a need or expectation for sending specific subnets and not just summarized routes, make sure that automatic summarization has been disabled.
A security concern of any routing protocol is the possibility of accepting invalid routing updates.
RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPF, IS-IS, and BGP can be configured to authenticate routing information.
=> Routers will only accept routing information from other routers that have been configured with the same password or authentication information.
CCNA Expl 2. Chapter 6.VLSM and CIDR
CCNA Exploration 2.Routing protocols and Concepts
RESUME.
Chapter 6. VLSM and CIDR
Classful IP addressing.
RIPv1 summarizes subnets to a single major network classful address when sending the RIPv1 update out an interface that belongs to another major network.
In 1993, IETF introduced Classless Inter-Domain Routing, or CIDR (RFC 1517).
CIDR allowed for:
~ More efficient use of IPv4 address space
~ Prefix aggregation, which reduced the size of routing tables
Classful IP addressing.
Class | Start | End | network portion of the address | Hosts per network | Networks |
Class A | 0.0.0.0 | 127.255.255.255 | 8 bits | 160777214 | 128 |
Class B | 128.0.0.0 | 191.255.255.255 | 16 bits | 65534 | 16384 |
Class C | 192.0.0.0 | 223.255.255.255 | 24 bits | 254 | 2097152 |
Multicast | 224.0.0.0 | 239.255.255.255 | |||
Experimental | 240.0.0.0 | 255.255.255.255 |
RIPv1 summarizes subnets to a single major network classful address when sending the RIPv1 update out an interface that belongs to another major network.
In 1993, IETF introduced Classless Inter-Domain Routing, or CIDR (RFC 1517).
CIDR allowed for:
~ More efficient use of IPv4 address space
~ Prefix aggregation, which reduced the size of routing tables
- RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPF, IS-IS and BGP
The network portion of the address is determined by the network subnet mask, also known as the network prefix, or prefix length (/8, /19, etc.).
CIDR uses Variable Length Subnet Masks (VLSM) to allocate IP addresses to subnets according to individual need rather than by class.
The ability for routes to be summarized as a single route helps reduce the size of Internet routing tables.
A supernet summarizes multiple network addresses with a mask less than the classful mask.
Classless routing protocols include the subnet mask with the network address in the routing update.
A supernet is always a route summary, but a route summary is not always a supernet.
Подписаться на:
Сообщения (Atom)