CCNA Exploration 2.Routing protocols and Consepts.
A loopback interface is a software-only interface that is used to emulate a physical interface.
- ideal for simulating multiple networks attached to the same router.

Null Interface -
R2(config)#ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
R2(config-router)#redistribute static
- Redistribution involves taking the routes from one routing source
and sending those routes to another routing source.
R2# debug ip rip
The show ip protocols command verifies that R2 is configured for RIPv1 but receives RIP messages for both versions.
R# show ip interface brief
R# show ip protocols
R# debug ip rip
R# ping
R# show running-config
The network statement does two things:
1. It enables the routing protocol to send and receive updates on any local interfaces that belong to that network.
2. It includes that network in its routing updates to its neighboring routers.
If there is a need or expectation for sending specific subnets and not just summarized routes, make sure that automatic summarization has been disabled.
A security concern of any routing protocol is the possibility of accepting invalid routing updates.
RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPF, IS-IS, and BGP can be configured to authenticate routing information.
=> Routers will only accept routing information from other routers that have been configured with the same password or authentication information.
RESUME.
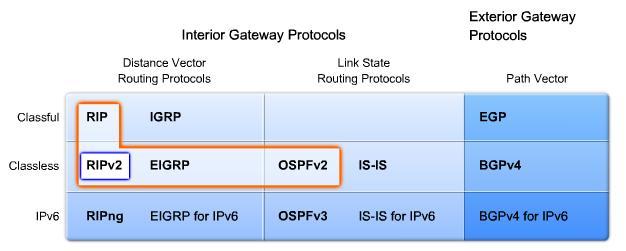
RIP v.1 | RIP v.2 |
Distance vector routing protocol | |
classful routing protocol | classless routing protocol |
do not include the subnet mask with the network address in routing updates, which can cause problems with discontiguous subnets or networks that use Variable-Length Subnet Masking (VLSM). | subnet masks are included in the routing updates |
following features and limitations: | |
~ Use of holddown and other timers to help prevent routing loops. ~ Use of split horizon or split horizon with poison reverse to also help prevent routing loops. ~ Use of triggered updates when there is a change in the topology for faster convergence. ~ Max. hop count limit of 15 hops, with the hop count of 16 signifying an unreachable network. | |
A loopback interface is a software-only interface that is used to emulate a physical interface.
- ideal for simulating multiple networks attached to the same router.

Null Interface -
R2(config)#ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
R2(config-router)#redistribute static
- Redistribution involves taking the routes from one routing source
and sending those routes to another routing source.
R2# debug ip rip
The show ip protocols command verifies that R2 is configured for RIPv1 but receives RIP messages for both versions.
By default, RIPv2 automatically summarizes networks at major network boundaries, just like RIPv1.
R3(config-router)#no auto-summary - To modify the default RIPv2 behavior of automatic summarization (RIPv2).
Because classless routing protocols like RIPv2 can carry both the network address and the subnet mask, they do not need to summarize these networks to their classful addresses at major network boundaries. Therefore, classless routing protocols support VLSM.
There are several ways to verify and troubleshoot RIPv2. Many of the same commands used for RIPv2 can be used to verify and troubleshoot other routing protocols.
1. Make sure all of the links (interfaces) are up and operational.
2. Check the cabling.
3. Check to make sure you have the correct IP address and subnet mask on each interface.
4. Remove any unnecessary configuration commands that are no longer necessary or have been replaced by other commands.
R# show ip route
R# show ip interface brief
R# show ip protocols
R# debug ip rip
R# ping
R# show running-config
The network statement does two things:
1. It enables the routing protocol to send and receive updates on any local interfaces that belong to that network.
2. It includes that network in its routing updates to its neighboring routers.
If there is a need or expectation for sending specific subnets and not just summarized routes, make sure that automatic summarization has been disabled.
A security concern of any routing protocol is the possibility of accepting invalid routing updates.
RIPv2, EIGRP, OSPF, IS-IS, and BGP can be configured to authenticate routing information.
=> Routers will only accept routing information from other routers that have been configured with the same password or authentication information.


Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий